
Newsletter Subscribe
Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter

The latest technology updates & more!

The use of data has grown in power for the global workforce. It’s necessary to convert vast amounts of organized and unstructured data into insightful and useful business knowledge for future development. As a result, many different big data tools handle and store data available in the present global market. Data has no relevance until it is transformed into knowledge and information that can help with business management. Big data innovation provides a business with a limitless array of features that deal with insight and forecasting to maximize efficiency and save costs.
Open-source database solutions are widely used by commercial organizations all over the world to handle their data. Due to their adaptability and ability to influence the platform’s progress, many businesses prefer to use open tools. Because of how quickly the world changes, a firm must invest in data analytics. Businesses worldwide now have a platform to create new database models employing large-scale analytics thanks to the fast-paced proliferation of information and technological improvements. Around the world, artificial intelligence is at the forefront of significant innovation.
Table of Contents
It is transforming our world and how we live at a never-before-seen pace. The emerging science analyses and forecasts machine and human behavior by sifting through enormous amounts of pertinent data. It alludes to the rapid growth of organized, semi-structured, and unstructured data volume. In 2018, it was anticipated to produce 50,000 Gb of data every second. The rapid growth of data has necessitated the need for effective data storage and processing.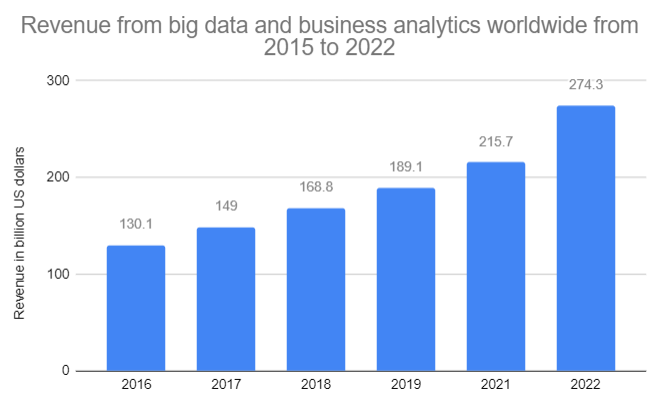
Big Data originates from numerous sources and is received in various formats. Big Data essentially just refers to all data. It can be explained in terms of data management problems that traditional databases are unable to address due to the growing volume, velocity, and variety of data. It originates from sensors, gadgets, video and audio equipment, networks, log files, transactional apps, the web, and social media, much of it produced in real-time and on a very large scale.
Big Data is a unique and more modern database than a typical database. Structured data may be stored and processed effectively in Standard Relational databases. The data is stored in a table and accessed and retrieved using SQL, a structured query language. Unstructured and semi-structured data are both included in big data. Numerous NoSQL Database types and tools are available to store and process Big Data. NoSQL databases are a particular category of the database. NoSQL databases are designed for data analytics with BigData, which includes text, photos, logos, and other types of data in XML and JSON formats. The creation of data-driven, intelligent applications benefits from the use of big data
The distinction between big data and databases is described below:
A wide range of Big Data tools and technologies are currently available on the market. They improve time management and cost-effectiveness for data analysis tasks. The top big data technologies and tools are listed below, along with some of their key features.
Spark, a unified analytics engine, was introduced in 2012 and was created specifically for using clustered computing to analyze big data. It has built-in machine learning algorithms, SQL, and data streaming modules, as well as high-level R, Java, Python, and Scala APIs (meaning you can use your preferred language when programming). Both stream and batch processing is supported. Since Spark is open-source and has so many built-in features, it can be applied to practically any industry that uses data science.
Like Spark, Hadoop is an open-source framework that includes a MapReduce engine for processing large amounts of data and a distributed file system for storing it. Even though the framework was introduced in 2006 and is slower than Spark, many businesses that have already used Hadoop won’t just drop it because another option exists.
There are advantages to Hadoop as well. It has been tried and tested to start. It is a solid and dependable piece of software, even if it is not the most user-friendly. Hadoop does not need supercomputers to be installed; it can be done on the majority of common commodity gear. Additionally, it is inexpensive to operate because it divides workload and storage. And if that’s not enough, Hadoop is still supported by a lot of enterprise cloud providers. Take IBM’s Analytics Engine, for instance. So, this is one tool you might still run upon while exploring data analytics.
Another free, open-source unified processing framework is Apache Flink. It enables batch and streams processing same, like Spark. Flink can process data significantly more quickly and with lower latency (or delay) than Spark, which measures latency in seconds rather than microseconds without delving too deep into the technical intricacies.
Google Cloud Platform combines several cloud computing services that Google itself utilizes for end-user products, including Google Search, Gmail, YouTube, and Google Docs, in order to compete with rival AWS (to name a few). The platform includes a number of big data tools incorporated inside it, including Dataflow (a managed streaming analytics service) and Data Fusion, despite not being a specific big data tool (for building distributed data lakes via the integration of on-premise platforms).
MongoDB is a versatile, scalable non-relational database (also known as a NoSQL database.) This basically implies that, rather than employing rows and columns, it is built for big unstructured data in the form of documents (as used in relational databases). MongoDB is a popular big data tool used by both tiny startups and established businesses.
It’s simple to set up and use. Additionally, it is schema-free (i.e., it does not have to adhere to a specific data type, which results in less work upfront) because it is intended to manage unstructured data. With over 175 million downloads, MongoDB is the most widely used NoSQL database in use, enabling all different types of users to access, alter, and analyze their unstructured data.
Sisense’s Big Data platform can be the best option for you if you’re looking for a big data tool that doesn’t require any specialized technical knowledge. Sisense bridges the gap between tools that manage huge data and tools that provide outstanding data analytics and visualization. How much you can alter is limited by the dashboard’s simple drag-and-drop interface. Sisense is a reliable business intelligence tool once it’s up and running and you’ve gotten used to its eccentricities, albeit it does have a few stability issues, and setup can be complicated.
With the aid of RapidMiner, data professionals of all skill levels will be equipped to quickly execute machine learning algorithms and develop data models. Through a process-focused visual design, it combines everything from data access and mining through preparation and predictive modeling. Although RapidMiner was developed in Java and can easily be connected with other Java-based applications, people who like to program from scratch may find the no-code approach to be a bit tough.
Big Data is not simply a technical trend; it is also a business practice that enables businesses to make proactive, data-driven decisions to boost sales and marketing team performance and revenue to compete in today’s market. Currently, global population expansion, technological advancements, and data volume growth are all occurring simultaneously. This proves the requirement and growing use of Big Data Analysis solutions.